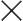By acting on the environmental, social, and economic dimensions of digital technology, responsible digital practices aim to positively affect each lever while minimizing ecological impact.
Why is this a topic of interest?
Because the digital ecosystem accounts for 3 to 4% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, surpassing even the civil aviation sector, which accounts for 2 to 3%.
Responsible Digital Practices: key areas
Digital Sobriety: less for more
This involves limiting the consumption of digital resources. Of the resources used in the digital sector, 76% are consumed during the extraction and manufacturing stages of digital equipment. As the saying goes, “The best waste is the one that doesn’t exist.” This mantra can be challenging to adopt in the age of all things digital and planned obsolescence (both physical and psychological: in 2020, 65% of French people would replace their smartphones even though the old one still works).
Eco-Design: Designing for longevity
Designing useful, usable, and used digital goods and services by reducing their weight, complexity, and update frequency. At this stage, including various stakeholders will be key.
End of life of devices: extending usefulness
Extending the lifespan of digital equipment by promoting repair, reuse, or recovery if they are no longer usable. At the European level, only 42.5% of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) is recycled. This figure drops to 17% worldwide.
Digital inclusion: for everyone, everywhere
Ensuring access to and use of digital technology for the greatest number of people, taking into account users’ needs, abilities, and preferences. This mainly concerns people with limited digital usage due to disability or digital illiteracy (in France, 15.4% of individuals aged 15 and over were affected by digital illiteracy in 2021).
Digital Ethics: user rights and freedoms
Respecting users’ rights and freedoms by ensuring the protection of their personal data, algorithm transparency, and combating discrimination. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), does that ring a bell?
“Great, additional costs. What’s the point?”
Far from being just a cost center, a responsible digital approach proves to be a real lever of performance and differentiation for companies.
Concrete benefits:
- Improving the Quality and Efficiency of Digital Services: By reducing their environmental impact, we also improve their technical performance, reliability, and security. By eco-designing digital services, we optimize their ergonomics, accessibility, and usefulness for users.
- Reducing Expenses and Risks Related to Digital Technology: By limiting the energy and resource consumption of digital technology, we decrease operational and maintenance costs. By anticipating regulatory changes and societal expectations on digital technology, we reduce the risks of financial penalties, legal sanctions, or missing a market shift.
Additional impacts:
- Externally: A responsible digital approach fits into a Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) policy. This strengthens the employer brand, trust, and loyalty of customers, partners, and employees. It also allows for standing out from the competition by offering innovative, sustainable, and ethical digital products and services. These concerns are particularly growing among young talents coveted by the IT sector.
- Internally: Responsible digital technology can be a factor of motivation and engagement for employees, giving meaning to their work and allowing them to participate in a collective project with a positive impact. It can also be a lever for learning and innovation, promoting the exchange of best practices, creativity, and experimentation.
As you can see, responsible digital technology is a lever of performance and differentiation for your company.
Where to start? Which direction to take and how to get there?
Talisker has designed the Positive Impact Label to help you! This tool allows you to assess the level of your IT department on Green-IT and more! We believe that the quality of relationships within the organization and with its ecosystem determines the success of the company. This is why Positive Impact focuses on five areas: Clients, Partners, Green IT, Employees, and Governance. Do you want to know more about the Positive Impact label or start the labeling process? Click here!